Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease of the tissues that support the teeth: the gum, the cementum, the periodontal ligament and the alveolar bone.
Periodontitis is diagnosed by probing the gums around the teeth and by evaluating the patient's x-rays.
Periodontitis is generally accompanied by these visible signs::
- Gingivitis which is an inflammation of the gum very often associated with bleeding ;
- Receding gums :when bony support is lost around the tooth and the tooth appears longer ;
- Loose teeth, a sign that is very concerning ;
- Black triangles or spaces between teeth ;
- Hypersensitive roots at the gum line.
To find out more about how we prefer to treat gum and periodontal disease, check out our page on Gum Care.
If you are concerned about gum disease, click here to make an appointment with one of our dentists who will recommend a natural solution that is appropriate for your situation.
Periodontitis destroys the bone that supports your teeth without pain. Here’s how to stop it:
GUM CARE :
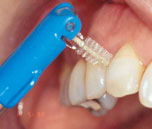
1.Use an interdental brush to disinfect between all teeth where it penetrates without resistance . Insert from the inside and the outside.
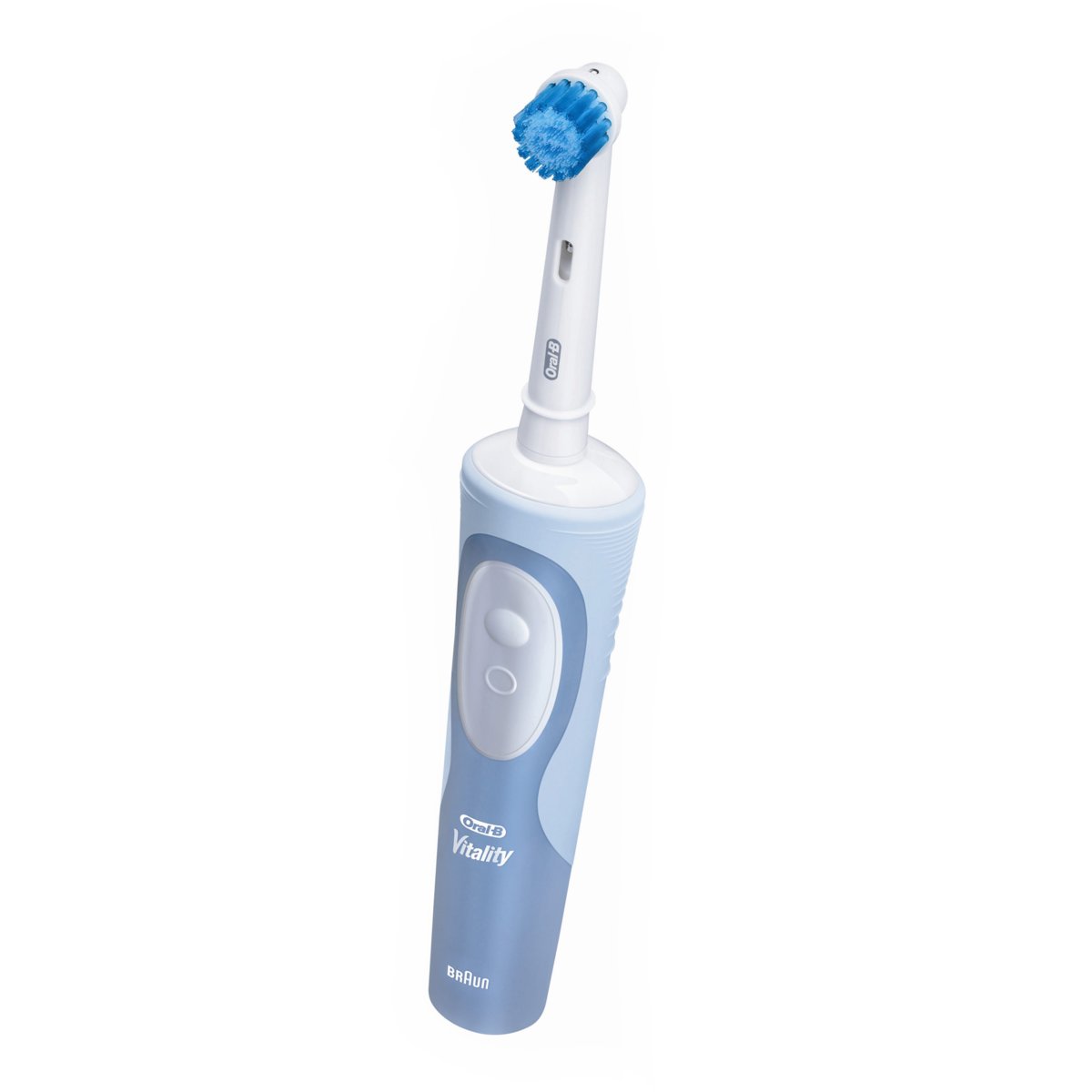
2.Brush morning and evening with an Oral-B/Braun automatic toothbrush – two minutes with Tooth&Gums toothpaste or a baking soda/ 3% peroxyde paste.
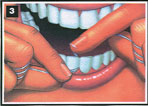
3. Use dental floss to clean between all teeth and behind your last teeth daily.
DIET:

1.Consume only whole foods
2.Mostly plants
3.In moderate quantities
4.Of organic quality

5.Supplement your diet with probiotics, unrefined sea salt and our Dentos bone and gum rebuilding formula: four capsules daily.
PROFESSIONNAL CARE:
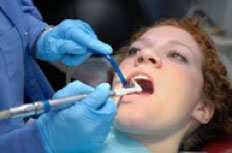
1.Once infected pockets have been eliminated, have your teeth cleaned every three to six months.
2.If required, we will refer you to a competent specialist.
3.To clean under bridges, consider irrigating your gums with a Water-Pik and Perio-Script antiseptic. This does not replace interdental brushing nor flossing.
